
Elasmobranch History
Elasmobranchs have a rich evolutionary history. Read on below to learn all about how they evolved.
What are elasmobranchs?
Sharks, rays and skates belong to the group Elasmobranchii, chimaeras which are a very close relative belong to the group Holocephali.
Elasmobranchii and Holocephali together form the taxonomic family called Chondrichthyes or Cartilaginous fishes. As the name suggests all of the members of this family have a simple skeletal structure formed from cartilage.
This distinguishes the family from other fishes whose skeletal structure is made up from bone. Some of the cartilaginous skeletal structures of Chondrichthyans are strengthened and hardened by the process of mineralisation (also referred to as calcification), whereby various salts are deposited into growing cartilage, but they do not have any “true” bone structure.

Elasmobranch Family Tree
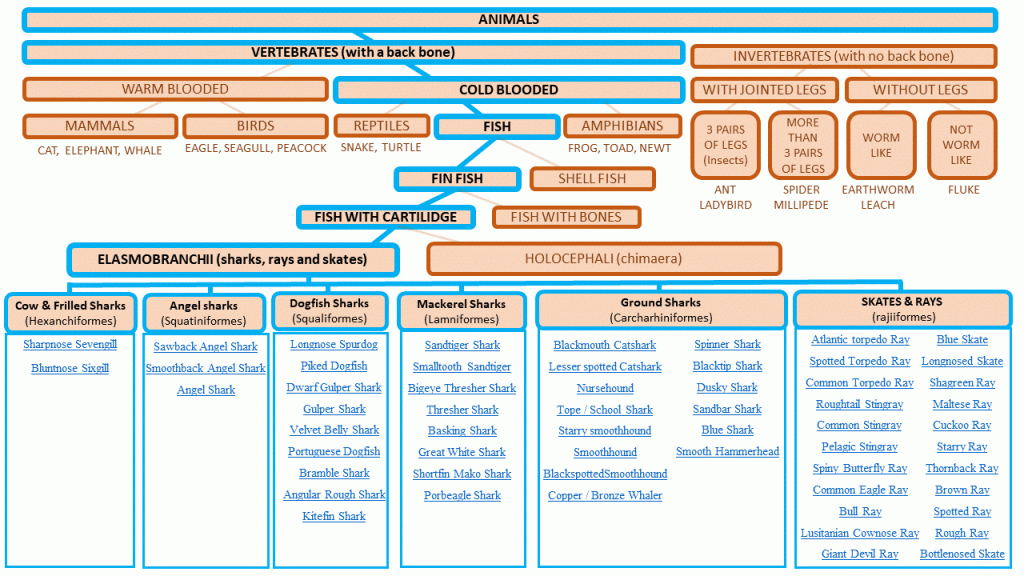
There are 8 orders of shark...
Extant or still living species of sharks are shown in taxonomic order in the diagram below. Sharks are spread across eight biological orders which are listed in roughly evolutionary order (primitive to modern), and the families and genera within the orders are listed in alphabetical order.

Hexanchiformes: – Cow and Frilled Sharks
Squaliformes: – Bramble Sharks, Dogfish Sharks, Gulper Sharks, Lantern Sharks
Pristiophoriformes: – Saw Sharks
Squatiniformes: – Angel Sharks
Heterodontiformes: – Bullhead and Horn Sharks
Orectolobiformes: – Carpet Sharks, Nurse Sharks, Whale Sharks, Wobbegongs
Lamniformes: – Basking Sharks, Mackerel Sharks, Thresher Sharks
Carcharhiniformes: – Catsharks, Hammerhead Sharks, Houndsharks, Requiem Sharks
